High-yield ETFs attract plenty of attention in the investing world thanks to their steady income and straightforward structure. If you’re hunting for a way to earn a higher payout than a typical savings account—or even some blue-chip stocks—these funds can be a pretty handy option. Many newcomers ask how they can make the most of these income-focused investments while managing risks, so here’s an all-in-one guide to help you get started.
Disclaimer: This article contains affiliate links. If you open an account through these links, I may earn a commission at no additional cost to you. Investing involves risk, including the possible loss of capital. eToro is not available in all countries. Eligibility depends on your region. Always consider your individual circumstances before investing.
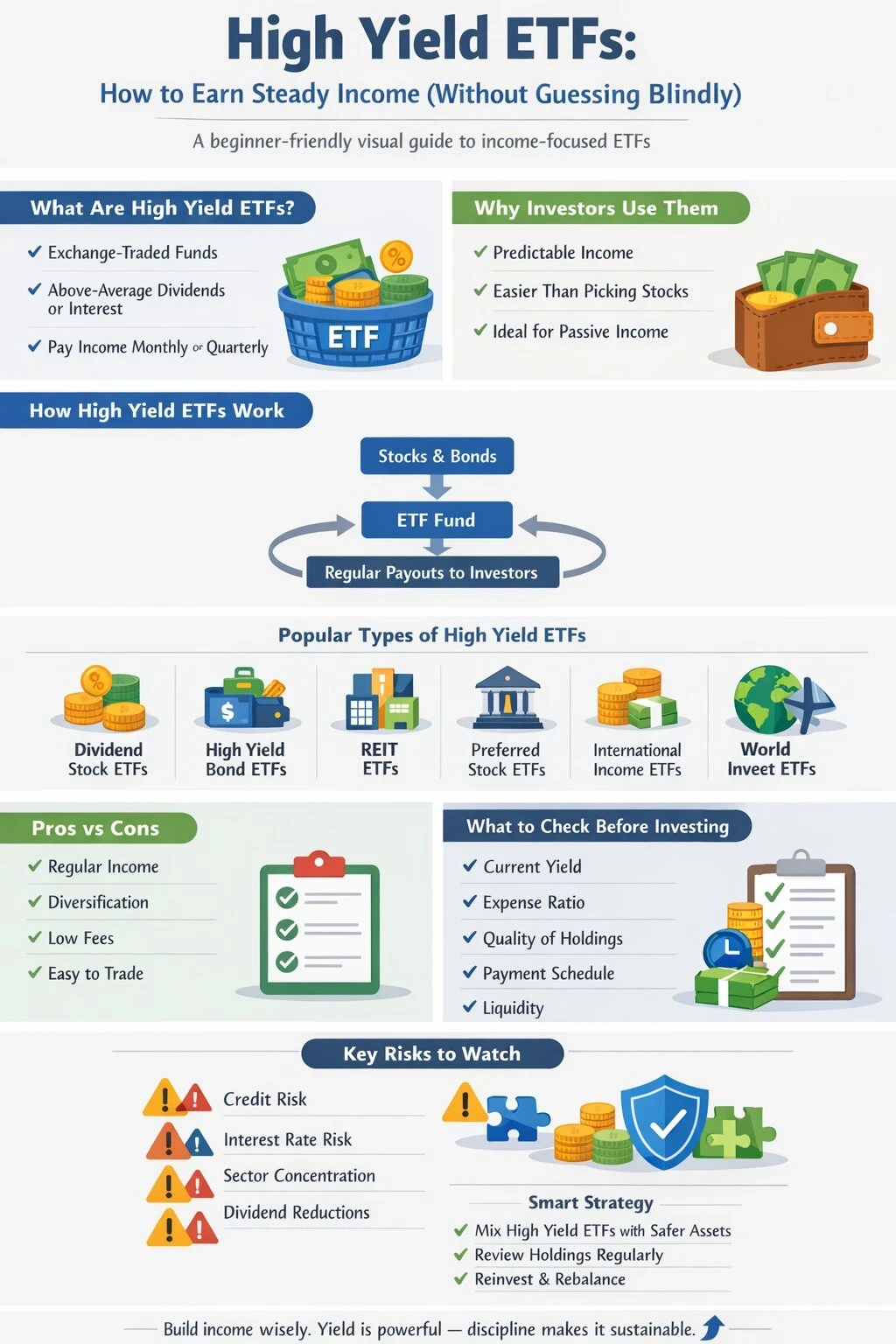
What Are High-Yield ETFs?
High-yield ETFs are exchange-traded funds that focus on investments paying above average yields, such as high-dividend stocks or bonds with higher interest payments. They trade on stock exchanges, meaning you can buy and sell them during market hours, just like regular stocks.
The main reason people choose these ETFs is their aim to generate regular income, which comes to you as dividends or interest payments right in your brokerage account. This appeals to retirees, folks building passive income streams, or anyone wanting extra cash flow.
Some trending types of high-yield ETFs include equity dividend funds, high-yield corporate bond funds, and REIT (Real Estate Investment Trust) ETFs. Each comes with unique advantages and risk levels, so it’s smart to know what you’re getting into before you invest.
How High-Yield ETFs Work
ETFs gather up a basket of assets, like stocks or bonds, then wrap them into one investment you can access easily through your brokerage account. High-yield ETFs use screens or strategies to select assets with higher-than-average dividend or interest payouts. That may mean focusing on companies with solid dividend histories or bonds from corporations with higher credit risk for bigger payouts.
The ETF provider collects the interest and dividends from portfolio holdings, then passes most of that income to investors, sometimes monthly or quarterly. These regular payouts can become a core income source, though amounts may change based on market conditions or fund performance.
Looking for more on ETFs in your portfolio? I recommend checking out these niche ETF strategies for some creative ways to build your investments.
Pros and Cons of High-Yield ETFs
Including high-yield ETFs in a portfolio brings real perks, but also a few drawbacks to keep in mind. Here’s a practical breakdown from what I’ve learned:
- Steady Income Flow: These ETFs help to keep cash flow predictable for anyone who wants money coming in at regular intervals.
- Easy Diversification: Buying a high-yield ETF means you own pieces of dozens or even hundreds of stocks or bonds—this spreads your risk out right away.
- Low Ownership Costs: Expenses for ETFs are usually less than those of similar mutual funds, which puts more income in your pocket.
- Liquidity: Since ETFs trade all day, you can buy or sell quickly if your plans mix up.
Some drawbacks you’ll want to keep in mind:
- Risk of High-Yield Assets: Higher yields sometimes signal that the market sees a higher risk of default or dividend cuts. That’s crucial because some funds invest in riskier corporate bonds or companies with financial trouble.
- Interest Rate Sensitivity: Bond-heavy high yield ETFs can lose value if interest rates rise, so your account might bounce around as rates switch up.
- Dividend Fluctuations: Payments can change depending on market health, and tough times might force a fund to cut payouts.
What to Look for When Picking a High-Yield ETF
Picking the right ETF feels more manageable when you focus on the details that matter. Here’s what I always check before clicking that buy button:
- Yield: Check the current yield, which shows how much the ETF pays compared with its share price. High yields catch your eye, but shouldn’t be your only focus.
- Expense Ratio: This percentage shows how much of your investment covers the ETF’s yearly costs. Lower expenses mean better returns for you.
- Holdings: See what the fund actually owns. Some ETFs hold more risk, focusing on junk bonds or struggling companies, while others stick with sturdy blue-chip stocks or high-quality bonds.
- Payment Schedule: Most high-yield ETFs pay dividends monthly or quarterly. If you rely on this income for bills, this detail matters.
- Liquidity: Popular funds see more trading, tighter price ranges, and smoother buying and selling.
I always cross-check these items when comparing funds. Informed research supports smart decisions, so I sometimes use a thorough ETF screener like the one at TradingView to zero in on yield, expense, and holdings.
Top Sectors and Strategies Inside High-Yield ETFs
Different high-yield ETFs target different sectors and strategies, and knowing what’s inside helps set your expectations. Here are some typical categories I see:
- Dividend Stock ETFs: These funds target large companies—think utilities, telecom, energy, or financials—that pay out higher than average dividends. Some stick to “dividend aristocrats,” stocks with a long run of raising payouts.
- High-Yield Bond ETFs: These funds buy bonds from companies rated below investment grade, sometimes called “junk bonds.” Risk is up, but so is your potential income.
- Real Estate ETFs (REITs): REIT ETFs buy into real estate-related assets. They often pay good dividends because they’re required by law to hand out most of their profits.
- Preferred Stock ETFs: Offering a blend between bonds and stocks, these funds come with regular payouts but generally more price stability than common stocks.
- International High Yield ETFs: These focus on global markets, letting you tap foreign companies or bonds with strong yields.
If you’re curious about how ETF approaches are changing, check out this post on the future of ETFs in a digital economy for more insight.
Risks to Watch and How to Manage Them
I often remind friends that no investment is risk-free, especially those promising bigger payouts. Here’s what to watch—and how I handle each issue:
- Credit Risk: High-yield bond ETFs can be volatile if the financial health of holdings shifts. A few defaults may reduce the fund’s value and payout.
- Interest Rate Risk: When rates rise, bond prices drop. Bond-heavy ETFs may see sharp decreases in value when this happens.
- Sector Concentration: Funds concentrated in one sector can swing hard if that space struggles. This is particularly true for some REIT or dividend stock ETFs.
- Dividend Cuts: A big company reducing its payout inside the ETF can suddenly lower the yield for everyone.
Balancing these risks is essential. I combine high-yield ETFs with safer funds or cash savings and avoid putting too much into any one ETF. By mixing things up and reviewing ETF holdings every few months, I can stay ready for surprises.
FAQs on High-Yield ETFs
Here are some of the most asked questions about starting with high-yield ETFs:
What’s the difference between a high-yield ETF and a regular dividend ETF?
A high-yield ETF usually targets the highest-paying assets (and often, higher risk), while regular dividend ETFs might focus more on long term stability and companies that consistently pay, even if at lower rates.
How do I buy a high-yield ETF?
Open a brokerage account at a platform like eToro or TradingView. Fund your account, then look up the ETF ticker symbol and place your order during market hours.
Are high-yield ETFs good for retirement income?
These funds can be a solid way to create ongoing income in retirement—just remember the risks. Many retirees use them alongside stable blue-chip stocks, government bond funds, or annuities for balance.
Do I pay taxes on high-yield ETF income?
Yes. Most income from high-yield ETFs is taxed as ordinary income or dividends. Tax rules depend on your country, so it’s smart to ask a tax professional or look up local rules.
Next Steps After Investing in High-Yield ETFs
Once you’ve selected your high-yield ETF and made your first investment, keep learning and tweaking your setup. Regularly review what you own, check payout schedules, and stay up to date with any fund updates. For extra advice, check out the next steps after investing in ETFs.
When used thoughtfully, high-yield ETFs can add solid returns to your passive income plan, making saving and building wealth a bit more enjoyable and effective.
If you want to take your returns up a notch, be on the lookout for new ETF ideas and strategies. This part of the investment world shifts and grows fast, and there’s always something fresh out there to consider.
Take your time to check out your options and build a portfolio that fits your financial goals. It’s a step-by-step adventure, and every bit of research you put in can pay off over time.
